Synthetic injection shaping represents a key production method which has transformed the production of plastic parts and elements across various sectors. Ranging from vehicles to consumer products, the versatility and effectiveness of this technique allow the creation of intricate patterns with elevated precision. With the pressure on businesses attempting to enhance output and minimize expenses, understanding the science behind synthetic injecting molding is essential for anyone keen in leveraging this service.
At its core, plastic injection molding entails heating plastic materials and injecting them into a form to form specific shapes. This technique facilitates for the swift manufacturing of premium products in bulk volumes, making it an attractive option for businesses seeking to expand their activities. By examining the varieties of substances used and the methods employed in this process, we can gain insights into how synthetic injection shaping solutions can meet the needs of contemporary production while maintaining environmental responsibility and innovation.
Comprehending Polymer Materials
Plastic substances are the cornerstone of plastic molding services, as they act a vital part in influencing the ultimate product's attributes and performance. Different types of plastics, including thermoplastic materials and thermosetting plastics, are used in molding processes. Thermoplastics can be reheated and reconfigured multiple times, making them versatile and ideal for a variety of applications. Common instances include PE and polypropylene, which are valued for their durability and lightweight characteristics.
The selection of material is guided by the intended use of the molded part. For example, advanced plastics like PC and polyamide provide enhanced durability and thermal resistance, appropriate for car and aviation uses. In contrast, performance plastics offer extra benefits, such as chemical resistance and shape retention, making them suitable for intricate designs and stressful environments. Understanding the properties and reactions of these substances is essential for choosing the right one for a specific project.
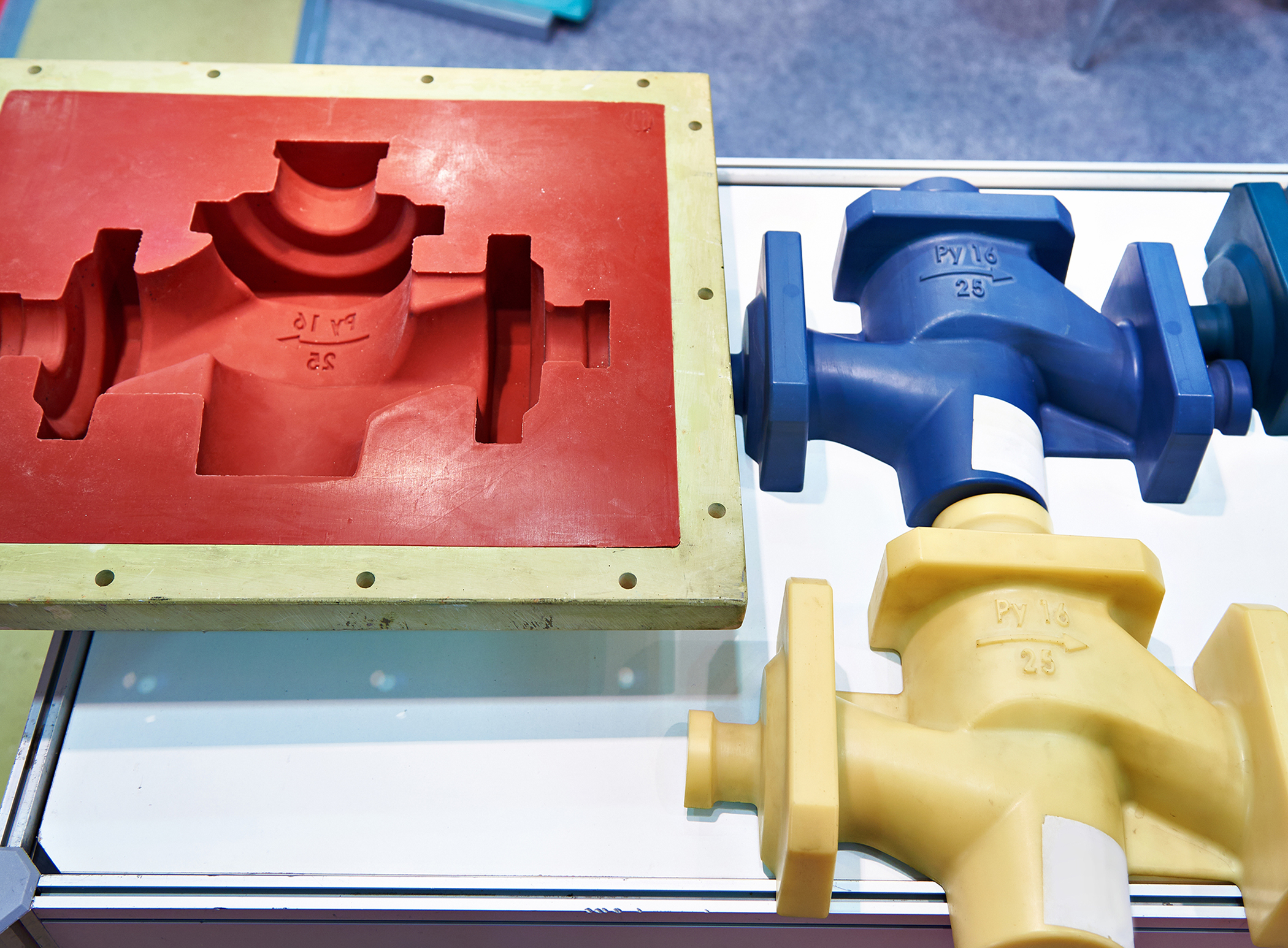
In furthermore to material kind, enhancers can be added to improve particular traits, such as color, pliability, or ultraviolet resistance. The molding service must carefully assess these elements during the design and production process to ensure that the ultimate result meets the specified standards. As advancements in material science progress, the selection of options available for injection molding expands, providing creative solutions for multiple industries.
Injection Molding Procedure Summary
The injection molding procedure starts with the preparation of unprocessed plastic materials, usually in the form of pellets. These granules are fed into a warm barrel where they are liquefied. The heat is carefully controlled to make sure the plastic attains the appropriate consistency for forming. Once the plastic is fully liquefied, it is forced into a mold space under intense pressure. This step is essential as it guarantees that the material occupies the whole mold and retains all the detailed details of the pattern.
After the liquid plastic is introduced into the mold, the cooling process starts. The mold is maintained at a precise heat level to enable the material to harden and take the shape of the mold. Cooling duration varies depending on the size and complexity of the part being produced. Once plastic injection molding service has solidified and hardened sufficiently, the mold opens, and the finished part can be removed. This part is then evaluated for quality, ensuring it meets the necessary criteria before proceeding to the next step.
Finally, any necessary additional processes are performed on the molded part, such as cutting, assembly, or finishing. The efficiency of the injection moulding procedure allows for large-scale production while maintaining consistency in quality. With advancements in technology, contemporary injection molding services can accommodate a wide range of materials and complex geometries, making it a preferred option across multiple industries.
Utilizations and Gains of Injection Molding
Injection molding is broadly used across numerous industries due to its flexibility and efficiency in producing intricate forms. It plays a crucial role in the manufacturing of automotive components, where precision and durability are necessary. From dashboard panels to intricate electrical housings, the ability to create light yet strong parts makes this technique a favored choice in the automotive field.
Additionally significant application of the plastic injection molding process is in the household goods industry. Everyday items such as playthings, tableware, and self-care products are typically produced using this approach. The process allows for large-scale manufacturing, making it economically viable while ensuring steady quality in each item manufactured. Additionally, the options in picking materials enables companies to meet specific market needs, ranging from resilience to aesthetics.
The benefits of this technique also extend to environmental considerations. Recent advances in the technological field have made it possible to use recovered materials in the injection molding process, lessening waste and supporting environmentally friendly practices. Furthermore, the eco-efficiency of these machines contributes to reduced manufacturing costs and a lowered carbon footprint, making it a responsible option for manufacturers aiming to align profitability with sustainability.
